by Alvaro Sanchez
Managing satellite capacity in multi-orbit ecosystems involves the coordination and optimization of resources across different orbital regimes, such as low-Earth orbit (LEO), medium-Earth orbit (MEO), and geostationary orbit (GEO). With the increasing number of satellites being launched into orbit, managing capacity has become more critical to ensure the efficient use of resources and avoid interference.
The most appropriate approach to managing satellite capacity is to use advanced software tools that can optimize the sharing and pooling of resources across multiple orbits. These tools can take into account factors such as satellite availability, coverage areas, data rates, and latency to maximize the efficiency of satellite resources. Moreover, these smart tools can balance and optimize satellite capacity ensuring that the available resources of a satellite across multi-orbit environments, such as its bandwidth and power, are used efficiently and effectively to meet the needs of its users. Managing the pool of satellite capacity dynamically involves allocating capacity to different types of users, and agreements based on their specific needs and priorities. For instance, FlexCap developed by INTEGRASYS, is the latest technology available in the market to automate capacity management efficiently, the key functionalities are divided into four main goals:
1. Dynamic Bandwidth allocation: Satellite capacity can be allocated dynamically based on the changing needs of different users or applications.
2. Capacity Leasing and flexible booking: Satellite operators can also lease capacity to different users or resellers, allowing them to monetize unused capacity or generate additional revenue from their satellite network. The tool can allocate the capacity leases in each satellite or transponder, to plan and organize the available capacity.
3. Customer contracts: Satellite operators can enter contracts with the customer, providing them with guaranteed capacity over a certain period. The cost and revenue of these contracts depend on the terms and conditions of the agreement, such as the duration, the quality of service, and the pricing model. FlexCap allows the user to upload the agreement information to plan de capacity in real-time.
4. Traffic shaping and capacity demand per hour: It can be used to optimize the performance of the satellite network. This involves prioritizing certain types of traffic, limiting bandwidth for certain users or applications, or shaping traffic to fit within the available capacity. For example, transactional, emergency response agencies, or military operations.
By dynamically managing the pool of satellite capacity, satellite operators can optimize the performance and efficiency of their multi-orbit networks while meeting the diverse needs of their users, and applications.
In addition to these technical solutions, regulatory frameworks and coordination mechanisms are also essential for managing capacity in multi-orbit ecosystems. International organizations such as the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) play a critical role in coordinating the allocation of radio frequencies and orbital slots to avoid interference and ensure the efficient use of resources within multi-orbit environments. It develops international regulations and standards for radio communication systems and satellite networks, and it coordinates the use of radio frequencies and orbital slots to prevent interference and ensure the efficient use of resources. This involves developing regulations and standards for different orbits, such as LEO, MEO, and GEO, and ensuring that satellite systems in different orbits do not interfere with each other. The ITU also manages the satellite filing process, which involves satellite operators submitting formal requests to the ITU for the use of specific frequencies and orbital slots.
However this process takes a lot of time, and resources not only from satellite operators, who apply to obtain a license but also from regulators, who need to review the process and give a pass or fail. To navigate the ITU filing process for a satellite launch license, satellite operators must seek assistance from experienced consultants or legal advisors who specialize in satellite communication and regulatory compliance. They also need to be aligned with the ITU and national regulatory authorities to ensure that their application complies with all relevant regulations and standards.
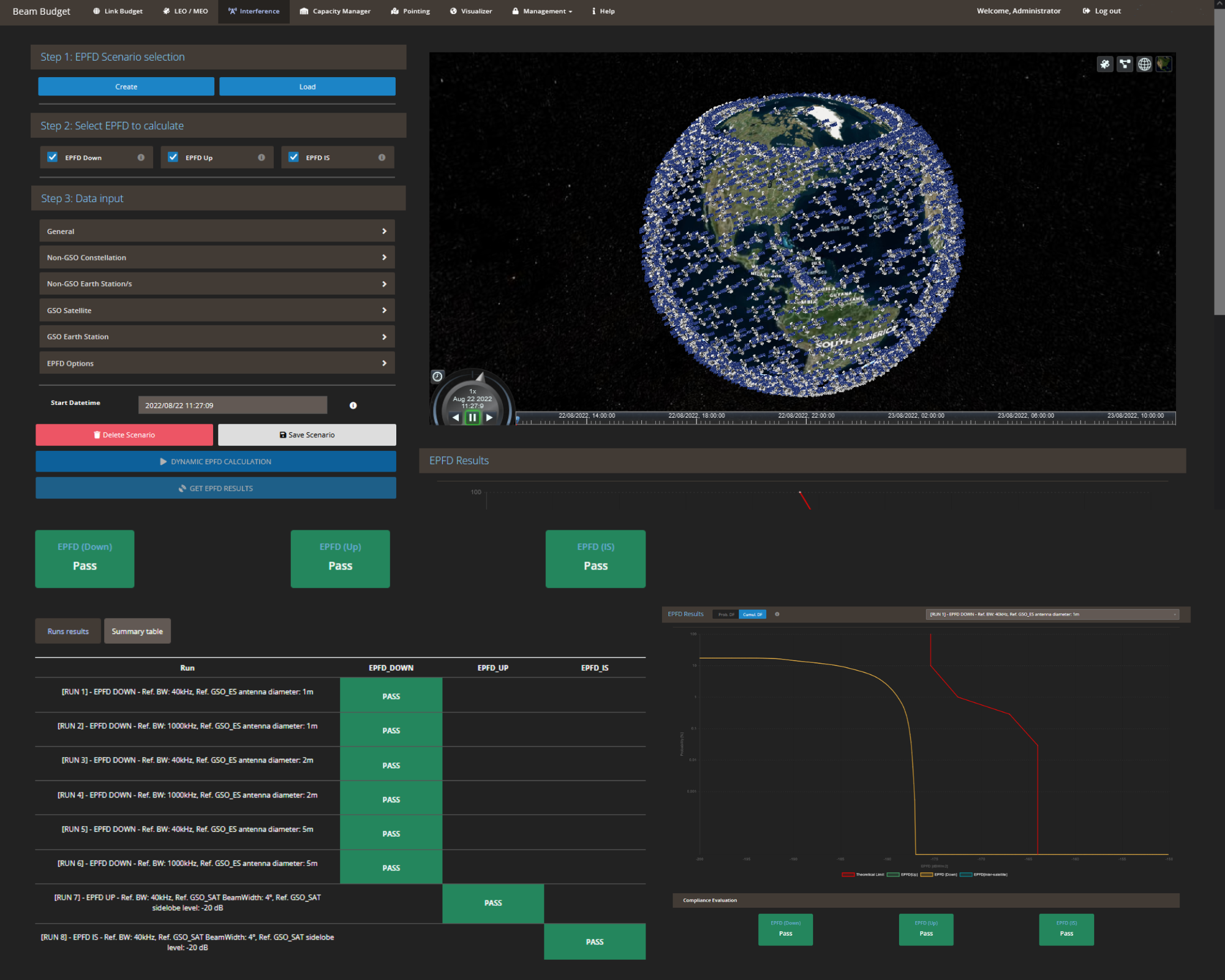
Nevertheless, the ITU filing process can be automated, using software applications that can review the requirements and test the calculations to adapt them to the regulations. For instance, VeryFiling the new ITU user-friendly EPFD calculation (up, down, inter-satellite) software aligned with ITU standards, allows satellite operators to test their constellations and adapt them to the ITU regulations before requesting approval. With Veryfiling, customers are certain to obtain a pass result with less skilled users, obtaining high-accuracy calculations with optimized processing times and complete reports. This technology has two modes, the industry mode which counts on an interface prepared to test their current setting and make the appropriate changes, to obtain the license, and the Regulator mode which is an easy interface that evaluates instantly if the filing is pass or fail. Additionally, VeryFiling can minimize expenses and internal resources, as the technology can be used by anyone, with a very low quantity of inputs, it is capable of extracting a customizable and complete report exportable to pdf or excel.
Overall, automating satellite capacity management, and ensuring a reliable satellite ecosystem, are essential, therefore software solutions are the greatest ally for satellite operators. These software solutions can help them to manage satellite capacity more efficiently and effectively, automate the ITU filing process, and optimize resource allocation across multi-orbit networks.
-----------------------------------------------

Alvaro Sanchez is the CEO of Integrasys and Marquess of Antella (Noble Title from 17th century in Spain). Alvaro is a Software and Industrial engineer by European University and holds a Master Degree in Management, Sales & Marketing from ESIC Business School. Alvaro during the last 10 years has worked at Integrasys as Management, Sales Director and Executive roles where he was very successful in growing the sales, revenue, profit and responsibilities within the company; and previous to that he was working at CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research as a RF Engineer measuring timing in a Nanosecond Synchronization for measuring the Neutrino Speed. The Noble Title that he hosts, is coming in his heritage from 1649 from his ancestor Nicolo Palavicino, given by Phillip IV in Sicily for the Antella region near Florence. He can be reached at alvaro.sanchez@integrasys-sa.com