by Bernardo Schneiderman
The use of small and medium satellites for applications such as remote sensing, observation, communication, and space exploration is expected to drive the growth of the Satellite Launch Vehicle market (SLVM) during the next decade.
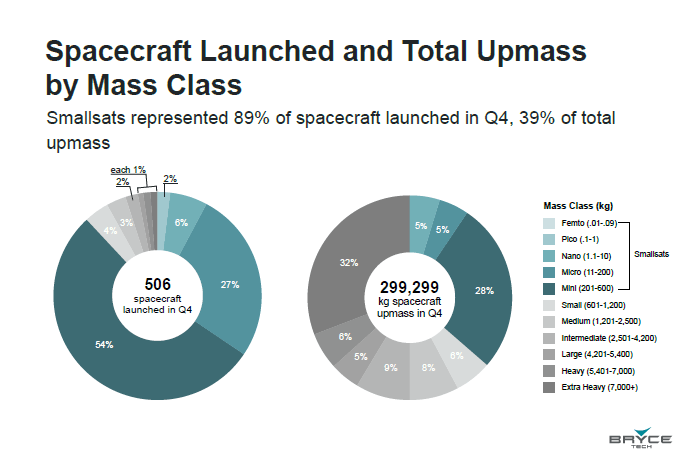
Analytics firm BryceTech which issues a quartely update on the launch market, reported that in the 4th quarter of 2022, Smallsats represented 89% of spacecraft launched 39% of total upmass (see graph). The number of satellites launched by application are the following: communications 80%, Remote Sensing 10%, Technology Development 7%, Scientific 1% and others 1%.
BryceTech reported that small satellites have broken records and are transforming space-architectures during the last 10 years. As defined by the US Federal Aviation Adminisration (FAA), 600 Kg and under reflect five smallest mass classes. Between 601 and 1200 Kg are considered Small Satellites and Medium Satellites are between 1,201 and 2,500 Kg.
 The 501-2,200 Kg satellite mass segment has the highest market share and is estimated to grow over the forecast years due to the rise in the number of small satellite constellations from various key manufacturers such as SpaceX, Amazon Kuiper, Cloud Constellation, Urthecast, ISRO, among others.
The 501-2,200 Kg satellite mass segment has the highest market share and is estimated to grow over the forecast years due to the rise in the number of small satellite constellations from various key manufacturers such as SpaceX, Amazon Kuiper, Cloud Constellation, Urthecast, ISRO, among others.
The land platform has the highest market penetration in the global SLVM during the next 10 years. The market growth is due to cost-effective launch and high success rate and recuperated part of the Launch Vehicle.
Smallsats represent 87% of spacecraft launched between 2013- 2022 and during 2022 represent 95% of spacecraft launched. A total number of 1736 Starlink and OneWeb Smallsat Satellites were launched in 2022 and the remaining 568 were other applications.
In regards to the major countries that are launching Smallsat USA are in the top with 87%, China 7%, India 2%, Russia 1% and others countries 3%.
In regards to the category of the Launch Vehicle in 2022 we have for the Micro-Small Launch Vehicle the following rockets (Electron, Vega, Long March 6 and 11 and LancherOne. For Medium we have Falcon 9, Soyuz 2.1, PSLV, Antares 230.
To give a snapshot of the key players in the market, we have profiled several companies in this article. The companies have been selected based on the stage they are in the market such as product portfolios, market penetration, and research and development initiatives. We reached out to several companies and featured the following companies in this article: Firefly Aerospace, Isar Aerospace, ABL Space Systems, RocketLab, Gilmour Space and Virgin Orbit.
Firefly Space
Firefly Aerospace Inc. is an American end-to-end space transportation company committed to providing economical and convenient access to space for small payloads through the design, manufacture, and operation of reliable launch and spacecraft vehicles. Firefly’s launch vehicles utilize common technologies, manufacturing infrastructure, and launch capabilities, providing LEO launch solutions for up to ten metric tons of payload. Combined with Firefly’s in-space vehicles, such as the Space Utility Vehicle (SUV) and Blue Ghost Lunar Lander, Firefly provides the space industry with a single source for missions from LEO to the surface of the Moon or beyond. Firefly is headquartered in Cedar Park, TX.
Launch Status: October 3, 2022 – Firefly Aerospace, , announced that its Alpha FLTA002 mission successfully reached orbit and deployed customer payloads, lifting off on October 1,2022 at 12:01am PST from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California.
With the success of this mission, Firefly is now the first company to launch and reach orbit from US soil in only its second attempt. Firefly also became the first and only US commercial space company with a rocket ready to take customers to space in the highly desired 1300kg payload lift class.
Alpha is an all-composite rocket that uses patented tap-off engine cycle technology, which reduces cost and improves efficiency while maintaining the strength and reliability of the rocket. During the mission, Alpha successfully completed all major technical milestones, including a two-burn maneuver, relighting the second stage during its first orbital flight.
Firefly is completing the Acceptance Testing Protocol (ATP) for its Alpha 3 vehicle in preparation for its upcoming NASA VCLS Demo 2-FB ELaNa 43 launch. In addition, Firefly continues the production of multiple rockets at its Texas manufacturing facilities using all the lessons learned from existing flights and testing. Firefly is scheduled for six Alpha launches to take customer payloads to space in 2023, and 12 more in 2024.
Isar Aerospace
Isar Aerospace based in Germany, was founded in 2018 to lower the entry barriers to space. By pushing the boundary as a platform for future technologies and competitiveness. As a launch service provider for small and medium-sized satellites is creating easy access to space for global customers. Offering the first fully privately funded European solution to meet the growing global demand, Isar Aerospace is driving commercial space across all continents.
Launch Status: On January 25, 2023 –Isar Aerospace, and U.S.-based Spaceflight Inc., announced they have signed a multi-launch services agreement. Under the agreement, Spaceflight secured one dedicated launch in 2026 to a sun-synchronous orbit taking off from Andøya, Norway and an option to add an additional dedicated launch to occur in 2025.
BL Space Systems
Founded in 2017, ABL Space Systems designs and manufactures the majority of its own infrastructure and launch materials. For whatever parts ABL outsources, the company maintains a firm grip, writing on its website that "not just our suppliers, but our sub-suppliers and investors are highly vetted and audited."
The company is headquartered in El Segundo, California, where much of its design and manufacturing take place alongside assemblies and system integrations. The company operates two facilities in the Mojave Desert — one at Edwards Air Force Base and the other at the Mojave Air and Space Port. ABL's Mojave Desert facilities focus on research and development, as well as engine and equipment testing. ABL also holds a suite of offices in Seattle "to be responsive to customer needs across geographies," according to the company's website.
ABL's RS1 rocket stands 88 feet (26.8 meters) tall, and is powered by nine of the company's E2 engines in its first stage and a singular E2 in its second. ABL describes the E2 rocket engine as "intentionally boring." The E2 is built, in part, using 3D-printed components that ABL produces in-house and is fueled by a choice combo of liquid oxygen and either RP-1 or Jet-A, which are both widely available forms of kerosene fuel. ABL is charging $12 million per RS1 launch.
Launch Status: Last Jan 18,2023 ABS planning to launch the RS1. After 10 seconds the stage 1 suffered complete loss of power. This caused a clean simultaneous shutdown of all nine engines. Stage 2 continued to operate more 2.63 seconds but the overall launch failed. Now ABL is investigating the reason for this failure but has already planned for Flight 2 after finding the problem with the Flight 1.
RocketLab
Founded in 2006, Rocket Lab is an end-to-end space company with an established track record of mission success. RocketLab delivers reliable launch services, satellite manufacture, spacecraft components, and on-orbit management solutions that make it faster, easier and more affordable to access space. Headquartered in Long Beach, California, Rocket Lab designs and manufactures the Electron small orbital launch vehicle, the Photon satellite platform and the Company is developing the large Neutron launch vehicle for constellation deployment. Since its first orbital launch in January 2018, Rocket Lab’s Electron launch vehicle has become the second most frequently launched U.S. rocket annually and has delivered 155 satellites to orbit for private and public sector organizations, enabling operations in national security, scientific research, space debris mitigation, Earth observation, climate monitoring, and communications. Rocket Lab’s Photon spacecraft platform has been selected to support NASA missions to the Moon and Mars, as well as the first private commercial mission to Venus. Rocket Lab has three launch pads at two launch sites, including two launch pads at a private orbital launch site located in New Zealand and a third launch pad in Virginia in the USA.
Launch Status: Jan 24, 2023 Rocket Lab USA, Inc. successfully launched its 33rd Electron rocket and first mission from Virginia. The “Virginia is for Launch Lovers' ' mission lifted o at 18:00 EST on January 24th from Rocket Lab Launch Complex 2 (LC-2) at Virginia Space’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport within NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility. The mission deployed three satellites to a 550 km orbit for leading radio frequency geospatial analytics provider HawkEye 360. Rocket Lab has now successfully deployed a total of 155 satellites to orbit from the Company’s three launch pads across the U.S. and New Zealand.
Gilmour Space
Gilmour Space is developing a range of Eris launch vehicles for LEO, MEO/GEO and LLO. Its maiden orbital flight will be from Australia this year, and is expected to be able to launch up to 1000 kg to LEO by 2025.
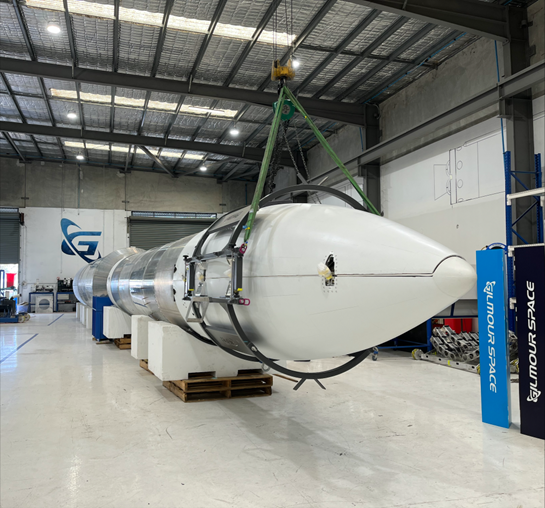 |
| Gilmour Space's Eris launch vehicle (image courtesy of Gilmour Space) |
"The need for responsive access to space and more frequent orbital launches has never been greater. Gilmour Space has identified this need and we will support the global rideshare market with the 'Caravan' missions onboard our Eris launch vehicles. These rideshares missions begin late in 2024 and will be a regular occurrence on our launch roadmap going forward," said David Jervis, Head of Sales at Gilmour Space.
Gilmour Space will provide launch services from our Bowen Orbital Spaceport in Queensland, Australia. "We are creating flexible launch solutions for dedicated and rideshare satellites to support global commercial and defense satellite customers. In the coming years there will be a regular cadence of Eris rockets launching from Australia to a variety of inclinations. Australia provides one of the most accessible and picturesque launch locations in the world and we are thrilled to provide the satellite market with a launch from 'Down Under' added Jervis.
Launch Status: "We are excited for our maiden test flight, which will launch in 2023. Do watch our social media pages for more details closer to the date. In addition to our production of launch vehicles, Gilmour Space is developing a small satellite bus called the G-Sat, a 100 kg-class modular, scalable and launch agnostic satellite bus, designed to support a wide variety of missions including a hosted payload mission “Kangaroo” which Gilmour Space plan to launch at the end of 2024, added Jervis.
Virgin Orbit
Founded by Billionaire Sir Richard Branson in 2017, Virgin Orbit began commercial service in 2021, and has already delivered commercial, civil, national security, and international satellites into orbit. Virgin Orbit’s LauncherOne rockets are designed and manufactured in Long Beach, California, and are air-launched from a modified 747- 400 carrier aircraft that allows Virgin Orbit to operate from locations all over the world in order to best serve each customer’s needs
Launch Status: Last June 2022 Virgin Orbit launched seven satellites into space oni its 'Straight Up' mission, that will support the United States Space Force’s STP-28A mission. The rocket was launched at the Mojave Air and Space Port. The Rocket Systems Launch Program (RSLP) and carry payloads for the Department of Defense (DoD) Space Test Program (STP). In January 2023, Virgin Orbit launched nine small satellites atop a rocket dropped from a 747 jumbo jet south of Ireland, but the booster suffered a failure during the climb to space and the payloads were lost, according company..
Conclusion
There are many other companies entering the SMLV market from various parts of the world including in emerging markets such as India. They are all trying to capitalize in the projected boom in small-and medium-size satellites to be launched in the next ten years. Frost & Sullivan forecasts an estimated launch demand for 11,746 small satellites for new constellation installations and replacement missions by 2030. Such demand would take the small-satellite launch services market past the U.S.$69 billion mark and present significant growth opportunities throughout the industry.
In order to keep up with market demand, Frost & Sullivan anticipates innovative solutions will be deployed across the value chain including launch, manufacturing, and supply chain. In such an evolving market it will be critical for market participants to develop long-term sustainable partnerships to maintain and establish robust business operations.
SpaceFund, a venture capital firm that specializes in the NewSpace economy, is tracking about 165 rocket companies from around the world. Nearly 75% are focused on designing and developing small launch vehicles. The ability to shrink sensors and other components into more compact payloads has really helped change the game for commercial launch providers. Smaller satellites require smaller rockets, which require less fuel. The economics are even better if the company employs reusable rockets such as SpaceX and Amazon's Blue Origin.
The next few years will see which companies will eventually rise to the top and those that will go by the wayside amid the intense competition in the SMLV market.
-------------------------------------------

Bernardo Schneiderman is a correspondent of Satellite Markets and Research and the Principal of Telematics Business Consultants. He can be reached at: info@tbc-telematics.com